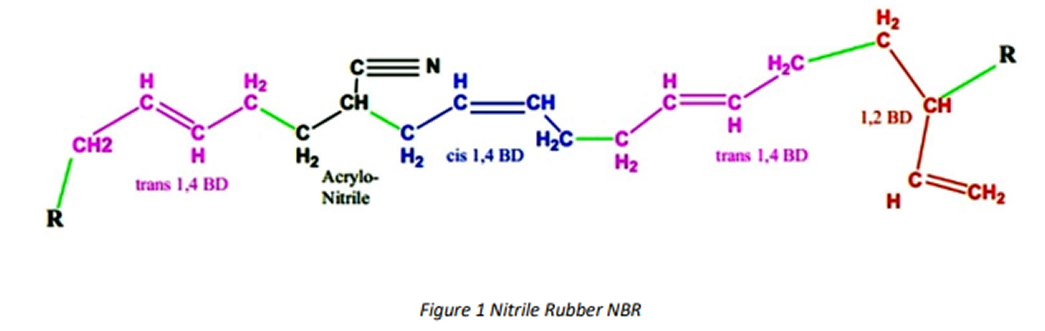
The current generation of cold NBR’s spans a wide variety of compositions. Acrylonitrile content ranges from 15% to 51%. Mooney values range from a very tough 110 to pourable liquids, with 20-25 as the lowest practical limit for solid material. They are made with a wide array of emulsifier systems, coagulants, stabilizers, molecular weight modifiers, and chemical compositions. Third monomers are added to the polymer backbone to provide advanced performance. Each variation provides a specific function.
Cold polymers are polymerized at a temperature range of 5 to 15°C, depending on the balance of linear-to-branched configuration desired. The lower polymerization temperatures yield more linear polymer chains. Reactions are conducted in processes universally known as continuous, semi-continuous and batch polymerization.
Crosslinked hot NBR’s are branched polymers that are further cross-linked by the addition of a di-functional monomer. These products are typically used in molded parts to provide sufficient molding forces, or back pressure, to eliminate trapped air. Another use is to provide increased dimensional stability or shape retention for extruded goods and calendered goods. This leads to more efficient extruding and vulcanization of intricately shaped parts as well as improved release from calender rolls. These NBR’s also add dimensional stability, impact resistance, and flexibility for PVC modification.
The addition of carboxylic acid groups to the NBR polymer’s backbone significantly alters processing and curing properties. The result is a polymer matrix with significantly increased strength, measured by improved tensile, tear, modulus and abrasion resistance. The negative effects include a reduction in compression set, water resistance, resilience and some low-temperature properties.
Nitrile rubbers are available with an antioxidant polymerized into the polymer chain. The purpose is to provide additional protection for the NBR during prolonged fluid service or in cyclic fluid and air exposure. When compounding with highly reinforcing furnace carbon black the chemical reactivity between the polymer and the pigment can limit hot air aging capability. Abrasion resistance is improved when compared with conventional NBR, especially at elevated temperatures. They have also been found to exhibit excellent dynamic properties.
NBR is and will continue to be a complex family of workhorse elastomers. The unique balance of oil, chemical, heat and cold resistance allow it to work well in a wide variety of automotive and industrial applications. The family is well differentiated to include general purpose types for cost-sensitive applications and specialty products (XNBR, Hot-Crosslinked NBR, HNBR) for more demanding service conditions.
Building a Sutainable Future for Your Organization and the Synthetic Rubber Industry
Download here

Address:
16360 Park Ten Place Suite 110
Houston, TX 77084
Contact Us:
+1 713 783 1703
info@iisrp.com