Emulsion polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber (E-SBR) is one of the most widely used polymers in the world today. The purpose of this article is to briefly review the history, production, chemistry, properties, and uses of E-SBR. Emulsion SBR is employed in many demanding applications, which enhance the quality of life and contribute significantly to our economy and standards of living.
Emulsion polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber (E-SBR) is one of the most widely used polymers in the world today. The purpose of this article is to briefly review the history, production, chemistry, properties, and uses of E-SBR. Emulsion SBR is employed in many demanding applications, which enhance the quality of life and contribute significantly to our economy and standards of living.
| Component | Parts by Weight | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold | Hot | ||||
| Styrene | 25 | 25 | |||
| Butadiene | 75 | 75 | |||
| Water | 180 | 180 | |||
| Emulsifier (FA,RA, MA) | 5 | 5 | |||
| Dodecyl mercaptan | 0.2 | 0.8 | |||
| Cumene hydroperoxide | 0.17 | - | |||
| FeSO4 | 0.017 | - | |||
| EDTA | 0.06 | - | |||
| Na4P2O7.10H2O | 1.5 | - | |||
| Potassuim persulfate | 0.3 | 0.3 | |||
| SFS | 0.1 | - | |||
| Stabilizer | Varies | - |
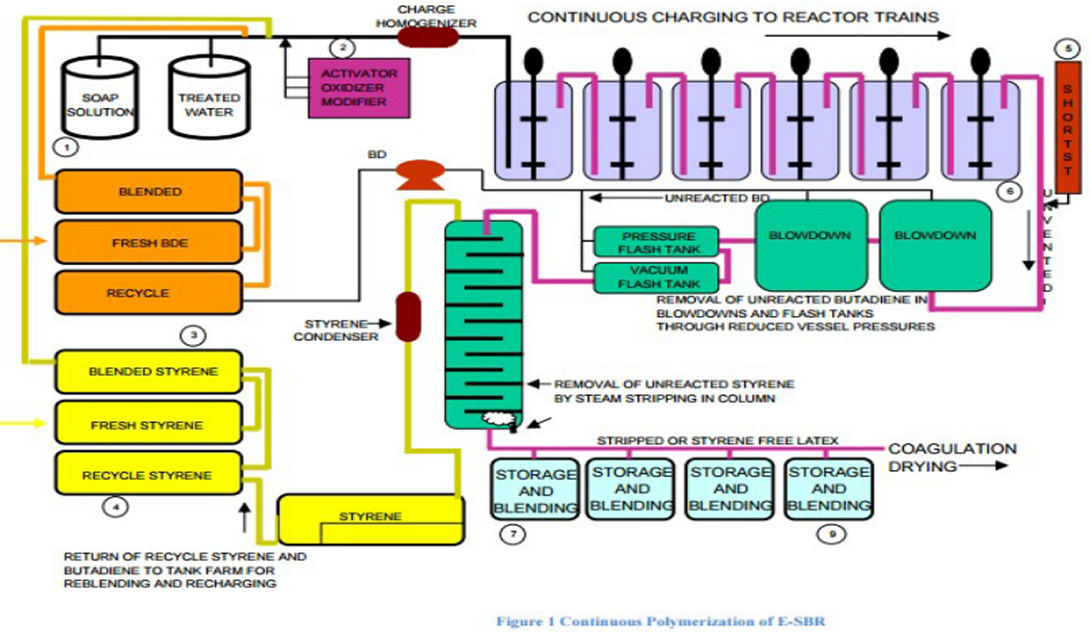
During polymerization, parameters such as temperature, flow rate, and agitation are controlled to get the right conversion. Polymerization is normally allowed to proceed to about 60% conversion in cold polymerization and 70% in hot polymerization before it is stopped by a shortstop agent that reacts rapidly with the free radicals. One common short-stopping agent is DEHA or diethyl hydroxylamine.
Once the latex is properly short stopped, the unreacted monomers are stripped off the latex. Butadiene is stripped by degassing the latex by means of flash distillation and reduction of system pressure. Styrene is removed by steam stripping the latex in a column. The latex is then stabilized with the appropriate antioxidant and transferred to blend tanks. In the case of oil-extended polymers or carbon black masterbatches, these materials are added as dispersions to the stripped latex.
The latex is then transferred to finishing lines to be coagulated with sulfuric acid, sulfuric acid/sodium chloride, glue/sulfuric acid, aluminum sulfate, or amine coagulation aid. The type of coagulation system is selected depending on the end-use of the product. Sulfuric acid/sodium chloride is used for general purpose. Glue/sulfuric acid is used for electrical grade and low water sensitivity SBR.
Sulfuric acid is used for coagulation where low-ash-polymer is required. Amine coagulating aids are used to improve coagulation efficiency and reduce production plant pollution. The coagulated crumb is then washed, dewatered, dried, baled and packaged.
There is a large variety of ESBR types based on the styrene content, polymerization temperature, staining or non-staining antioxidants, oil and carbon black content. Each of these basic classifications includes a variety of SBR polymer variations with respect to Mooney viscosities, coagulation types, emulsifier type, oil levels, and carbon black types and levels. The basic groups of ESBR are:
| Series | Types | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | Hot polymerized polymers. | ||||
| 1500 | Non-extended cold polymerized polymers. | ||||
| 1600 | Non-oil-extended cold carbon black masterbatches. | ||||
| 1700 | Cold oil-extended polymers. | ||||
| 1800 | Cold oil-extended carbon black masterbatches. | ||||
| 1900 | Miscellaneous high styrene resin masterbatches. |
E-SBR is predominantly used for the production of car and light truck tires and truck tire retread compounds. A complete list of the uses of SBR includes house are mats, drain board trays, shoe sole and heels, chewing gum, food container sealants, tires, conveyor belts, sponge articles, adhesives and caulks, automobile mats, brake and clutch pads, hose, V-belts, flooring, military tank pads, hard rubber battery box cases, extruded gaskets, rubber toys, molded rubber goods, shoe soling, cable insulation and jacketing, pharmaceutical, surgical, and sanitary products, food packaging, etc. The typical applications of E-SBR polymers are tabulated in Table 4 below.
| Hot Polymers | Cold E-SBR | High Styrene Masterbatch |
Black Masterbatch |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unextended | Oil Extended | ||||
| ADHESIVES | |||||
| Type & Label | X | X | |||
| Caulking | X | ||||
| Laminating | X | X | |||
| Mastic | X | ||||
| Panel | X | ||||
| Pressure Sensitive | X | X | |||
| Sealant | X | ||||
| Sprayable (Crosslinked) | X | ||||
| Wall Tile | X | ||||
| AUTOMOTIVE | |||||
| Tire Treads | X | X | |||
| Apex/Rim/Flange | X | ||||
| Bead | X | X | |||
| Carcass | X | X | |||
| Retread | X | X | X | ||
| Racing Tires | X | X | |||
| Mats | X | X | X | X | |
| MISCELLANEOUS | |||||
| Mechanical Goods | X | X | X | X | X |
| Rolls | X | X | X | ||
| Gaskets | X | X | X | X | |
| Belts/Hoses | X | X | |||
| Hard Rubber Goods | X | X | |||
| Cove Base | X | X | |||
| Floor Tiles | X | X | X | X | |
| Hot Polymers | Cold E-SBR | High Styrene Masterbatch |
Black Masterbatch |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unextended | Oil Extended | ||||
| MISCELLANEOUS Continued… | |||||
| Footwear | X | X | X | ||
| Sponge | X | X | |||
| Wire & Cable (Low Ash) | X | X | |||
Building a Sutainable Future for Your Organization and the Synthetic Rubber Industry
Download here

Address:
16360 Park Ten Place Suite 110
Houston, TX 77084
Contact Us:
+1 713 783 1703
info@iisrp.com